It is not about suppressing anger. It is about understanding it, controlling it, and expressing it in a healthy way. In today’s fast-paced academic and family environments, unmanaged anger affects learning, relationships, and mental well-being.
For students, anger reduces concentration and memory.
For parents, it disrupts the home environment.
For teachers, it affects classroom control and communication.
Learning anger management techniques helps individuals respond thoughtfully instead of reacting emotionally.
What is Anger Management?

Anger management refers to the ability to recognize signs of anger and use strategies to remain calm and in control. It involves emotional awareness, self-regulation, and practical techniques to handle frustrating situations.
Anger is natural. Poor handling of anger is harmful.
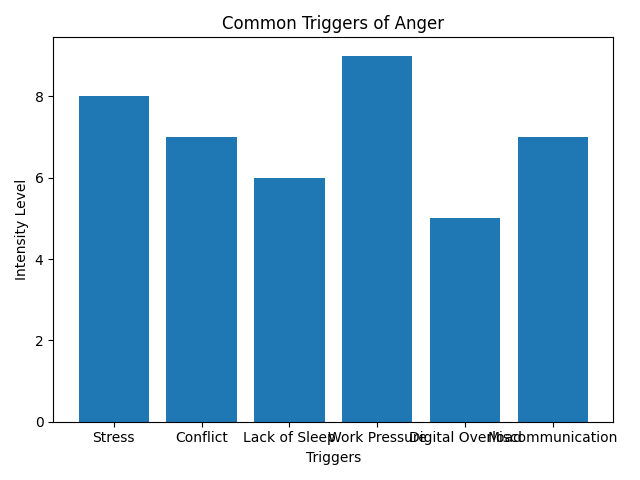
Why Anger Happens: Psychological Triggers
| Trigger | Example in Students | Example in Parents | Example in Teachers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stress | Exams, homework pressure | Work-life balance | Classroom discipline |
| Lack of sleep | Irritability | Fatigue | Reduced patience |
| Miscommunication | Peer conflict | Family arguments | Student misunderstanding |
| Unrealistic expectations | Fear of failure | High expectations | Performance pressure |
| Digital overload | Gaming, social media | Screen fatigue | Mental burnout |
Understanding triggers is the first step in anger management.
Signs That Anger is Becoming a Problem

Shouting frequently
Physical restlessness
Negative thoughts
Regret after reacting
Headaches or tension
Difficulty concentrating
These signs indicate the need to practice them before it affects mental health.
The Anger Cycle (Visual Flow)
Trigger → Thought → Emotion → Reaction → Consequence
If you control the thought, you control the reaction. This is the core principle of anger management.
10 Effective Anger Management Techniques

1. Pause and Breathe
Take 10 deep breaths before speaking. This simple step reduces emotional intensity.
2. Count to 20
Delays immediate reaction and gives the brain time to think logically.
3. Identify the Real Cause
Ask: Why am I actually angry? Often, the reason is deeper than the situation.
4. Use Calm Words
Replace shouting with assertive communication.
5. Physical Movement
Walking, stretching, or washing your face cools the body.
6. Avoid Immediate Decisions
Never decide or punish when angry.
7. Write It Down
Journaling emotions helps release mental pressure.
8. Practice Regular Sleep Routine
Lack of sleep increases irritability.
9. Reduce Screen Time
Digital fatigue increases emotional reactions.
10. Practice Gratitude
Positive thinking reduces frequent anger triggers.
Practicing these regularly builds strong anger management skills.
Anger Management for Students
Students often struggle with peer pressure, exams, and expectations.
| Situation | Wrong Reaction | Better Reaction (Anger Management) |
|---|---|---|
| Low marks | Crying, shouting | Review mistakes calmly |
| Peer teasing | Fighting | Inform teacher, ignore |
| Homework pressure | Frustration | Break into small tasks |
Students who learn how to perform better academically and socially.
Anger Management for Parents

Children learn emotional behavior from parents. Calm parents create calm children.
Avoid scolding in anger
Speak after calming down
Listen before reacting
Model patience
Anger Management for Teachers
Teachers handle multiple students daily, making emotional control essential.
Take micro-breaks between classes
Practice deep breathing
Avoid public anger display
Use positive discipline
Long-Term Benefits of Anger Management
| Area | Improvement |
|---|---|
| Mental health | Reduced stress and anxiety |
| Relationships | Better communication |
| Academics | Improved focus |
| Discipline | Better decision-making |
| Confidence | Emotional control |
Consistent management practice improves overall personality.
Daily 5-Minute Anger Management Routine
| Time | Activity |
|---|---|
| Morning | 2 minutes deep breathing |
| Afternoon | Short walk or stretch |
| Evening | Reflect on emotional moments |
| Night | Gratitude journaling |
Small daily habits make anger control natural over time.
Common Mistakes People Make
Suppressing anger instead of expressing it calmly
Reacting instantly
Holding grudges
Blaming others
Ignoring emotional health
These habits weaken management efforts.
When to Seek Help?
If anger leads to:
Physical aggression
Constant regret
Relationship damage
Sleep issues
Professional counseling can help develop structured anger management strategies.
Conclusion
It is a life skill that benefits students, parents, and teachers alike. It improves emotional intelligence, strengthens relationships, and enhances focus.
Anger cannot be removed from life, but it can be controlled with awareness, patience, and practice.
The goal is not to stop feeling angry.
The goal is to respond wisely instead of reacting emotionally.
FAQs on Anger Management
Q1. Is anger always bad?
Ans: No, Anger is natural. Mismanaging it is harmful.
Q2. How can students practice anger management at school?
Ans: By pausing, breathing, and informing teachers instead of reacting.
Q3. Can anger affect academic performance?
Ans: Yes, Anger reduces concentration and memory retention.
Q4. How can parents teach anger management to children?
Ans: By modeling calm behavior and encouraging communication.
Q5. How long does it take to develop anger control?
Ans: With daily practice, visible changes appear within 21–30 days.
Q6. Is shouting a good way to release anger?
Ans: No, It damages relationships and increases stress.









