Understanding the learning theories in education meaning is essential for enhancing how children learn, how teachers teach, and how parents support learning at home. Learning theories form the backbone of modern education by explaining how students absorb, process, and retain information.
Whether you’re a parent helping with homework, a teacher planning lessons, or a student trying to understand your own study habits, knowing the learning theories in education meaning equips you with tools to improve outcomes, motivation, retention, and engagement.
What Is the Meaning of Learning Theories in Education?

At its core, the learning theories in education meaning refers to structured frameworks that explain how humans learn. These theories help educators understand:
How information is acquired
How knowledge is retained
How motivation affects learning
How cognitive processes develop
Learning theories answer questions like: “Why do students learn differently?” and “How can teachers design effective instruction?”
Why Learning Theories Matter in Education
| Purpose | Educational Impact |
|---|---|
| Understand individual differences | Personalized learning |
| Improve teaching strategies | Better academic performance |
| Enhance motivation | Higher student engagement |
| Promote meaningful learning | Long-term retention |
| Build critical thinking | Better problem-solving skills |
Understanding the learning theories in education meaning allows teachers to plan lessons with the learner in mind — not just the curriculum.
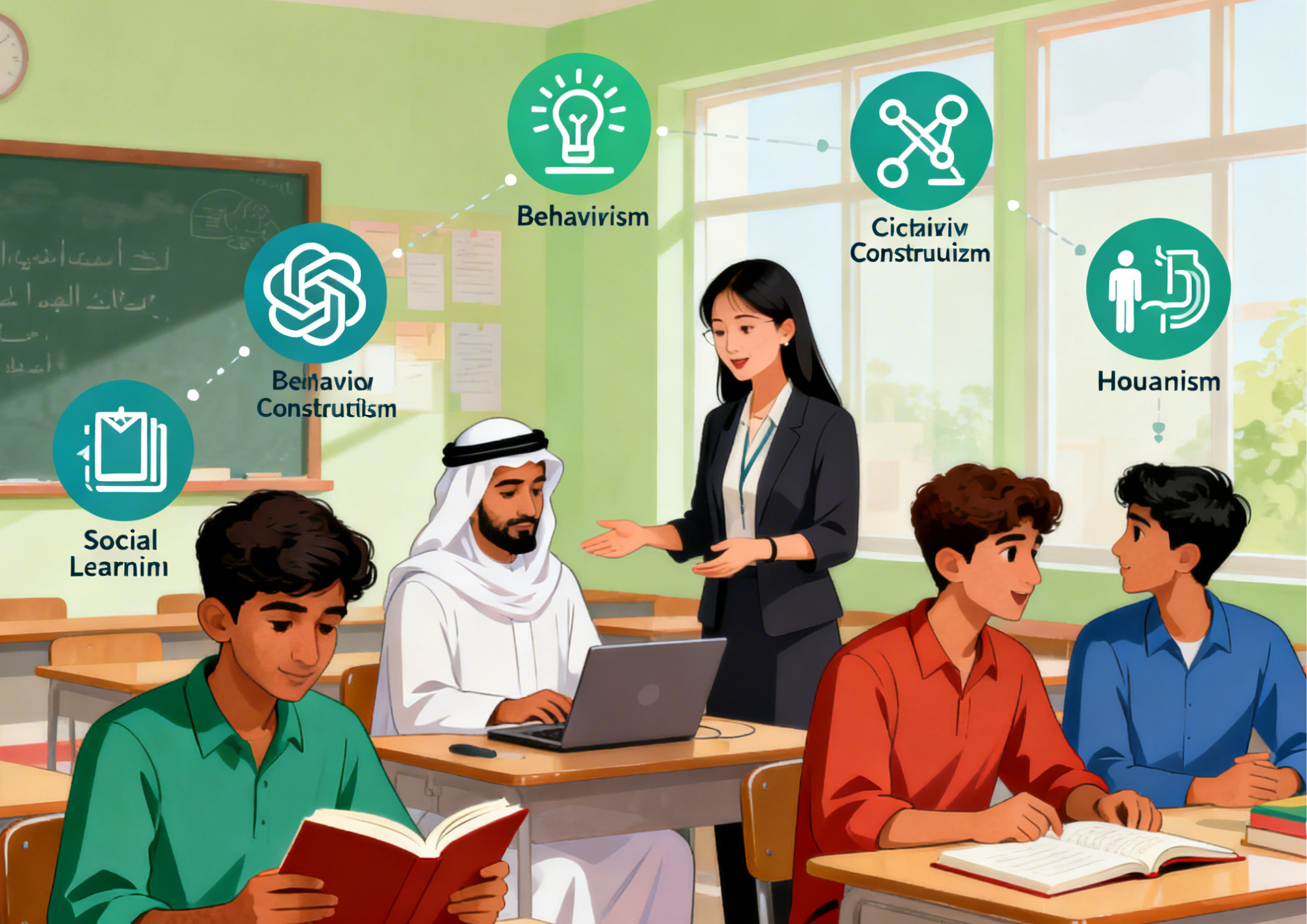
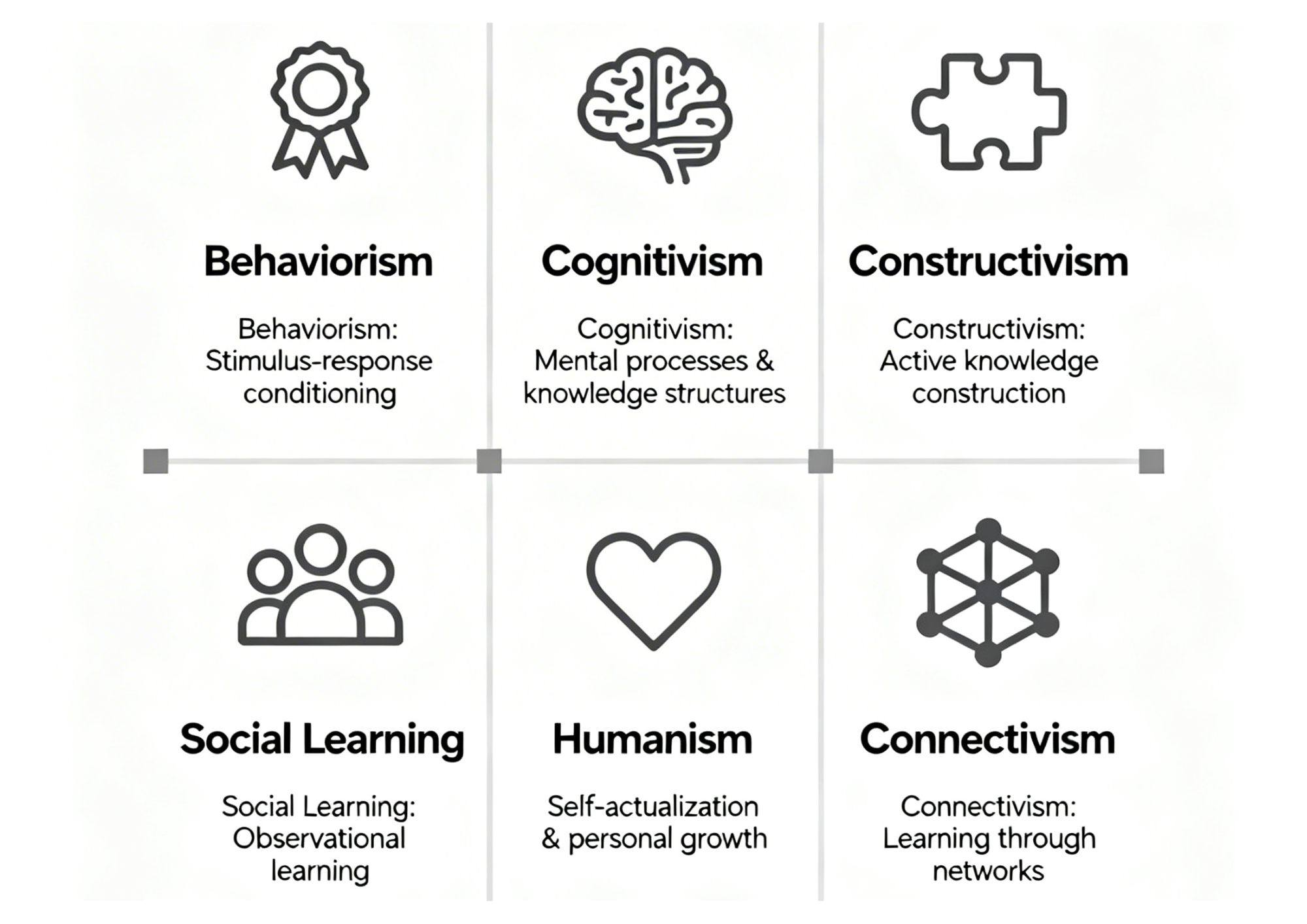
Major Learning Theories in Education and Their Meaning
Below is a table summarizing the most influential theories:
| Learning Theory | Core Idea | Practical Classroom Use |
|---|---|---|
| Behaviorism | Learning is change in observable behavior due to stimuli | Reward systems, drill practice |
| Cognitivism | Focuses on internal mental processes | Concept maps, structured play |
| Constructivism | Learners construct knowledge through experience | Project-based learning |
| Social Learning | Learning occurs by observing others | Group work, modeling behavior |
| Humanism | Emphasizes personal growth and self-direction | Self-paced learning, reflection |
| Connectivism | Learning through networks and technology | Online research, collaboration tools |
Each theory contributes a unique perspective on how learning happens.
1. Behaviorism — Learning Through Response and Reinforcement
Meaning: Behaviorism views learning as a change in behavior caused by external stimuli. Learning occurs when positive behavior is reinforced.
Example: Teachers using praise, tokens, or points to encourage participation.
In classrooms, behaviorism helps structure routines and reinforce good study habits.
2. Cognitivism — Learning Through Mental Processes
Meaning: Cognitivism focuses on understanding how the brain processes information — including memory, thinking, and problem solving.
Example: Teaching students how to use concept maps to organize information.
Cognitive strategies help learners become active participants in their own education.
3. Constructivism — Learning as Active Construction
Meaning: Constructivism asserts that learners build knowledge through experience, reflection, and connection to prior understanding.
Example: Group projects where students lead the learning process.
This theory strongly influences project-based learning and inquiry-based instruction.
4. Social Learning Theory — Learning Through Observation
Meaning: Proposed by Albert Bandura, this theory emphasizes that people learn by watching others.
Example: Peer tutoring and cooperative learning groups.
Observational learning boosts collaboration and modeling.
5. Humanistic Theory — Learning With Purpose and Self-Growth
Meaning: Humanistic learning theories focus on the individual’s potential and holistic development.
Example: Encouraging self-reflection and goal-setting.
This theory supports emotional wellbeing alongside academic growth.
6. Connectivism — Learning in the Digital Age
Meaning: A modern theory for the internet era, connectivism says learning occurs through networks and connections.
Example: Collaborative online platforms, research groups, and digital communities.
With technology becoming central to education, connectivism shapes how students learn today.
Visual: Learning Theories Comparison
Below is a simple conceptual chart showing how these theories relate to learner focus:

This flow shows progression from teacher-directed to learner-centered and network-oriented approaches.
How Learning Theories Affect Students, Parents and Teachers

For Students:
Helps build self-awareness of how they learn best
Encourages effective study habits
Supports critical thinking skills
For Parents:
Offers insight into learning behaviors
Helps parents support homework and motivation
Reduces frustration and conflict at home
For Teachers:
Improves lesson planning
Enhances classroom management
Promotes diverse instructional strategies
Internal Link Opportunity

Understanding different learning needs also helps when choosing environments that support growth — for example, why some students thrive in structured environments like Boarding Schools in India, where routines, peer learning, and holistic instruction align with various learning theories.
👉 Read more: Boarding Schools in India: Top Institutions, Benefits & Choosing Guide
Applying Learning Theories in the Classroom
| Theory | Classroom Strategy |
|---|---|
| Behaviorism | Reward charts, positive feedback |
| Cognitivism | Graphic organizers, memory cues |
| Constructivism | Projects, experiments |
| Social Learning | Group activities, peer review |
| Humanism | Journaling, self-assessment |
| Connectivism | Online discussions & blogs |
Case Study: How Students Benefit

A 14-year-old struggling in math used a cognitivist strategy — flashcards and concept maps — which improved retention. A group project based on constructivist principles helped boost engagement and grades.
FAQs on Learning Theories in Education
Q1. What is the meaning of learning theories in education?
Ans: The meaning of learning theories in education refers to frameworks that explain how knowledge is acquired, processed, and retained.
Q2. Why are learning theories important for teachers?
Ans: They guide how teachers plan instruction, motivate students, and assess learning.
Q3. How do learning theories help students learn better?
Ans: They help students understand their own learning preferences and use strategies to improve retention and engagement.
Q4. Can parents use learning theories at home?
Ans: Yes — parents can support homework, motivation, and emotional support based on learning styles and theories.
Q5. How are learning theories used in modern digital learning?
Ans: Connectivism plays a big role, as students learn through networks, online platforms, and peer collaboration.
Q6. Are learning theories only for educators?
Ans: No, understanding learning theories benefits students, parents, and teachers alike.
Conclusion
The learning theories in education meaning is not just academic jargon. It underpins how students learn, how teachers teach, and how parents support growth. Each theory offers unique insights:
Behaviorism helps reinforce good habits
Cognitivism strengthens mental processing
Constructivism fosters deep understanding
Social theory supports collaboration
Humanism nurtures self-direction
Connectivism prepares learners for a digital world
By applying these ideas thoughtfully, education becomes meaningful, engaging, and effective for all learners.
Understanding learning theories in education meaning empowers students, teachers, and parents to create smarter, happier, and more successful learning environments.









