We’ll be honest with you. LAMP is a weird acronym- Learning Management Systems. A mouthful, right?
Despite the complexity of the language itself, it’s not hard to see how similar LMSs and learning management systems are. The main differences are in their origin and the audience they serve. We’ll dive into each of these below.
All things listed are existing and independent technologies that have been around in some form or another for decades.
ALSO READ : Teaching digital literacy
What are Learning Management Systems (LMS)?

LMSes are advantageous to various enterprises, including for-profit businesses and institutes of higher learning. A learning management system is primarily for knowledge management (KM). Knowledge management (KM) is obtaining, arranging, disseminating, and analysing an organisation’s knowledge of its assets, documentation, and human capital. However, the LMS’s precise function will change depending on the organisation’s training objectives and strategy.
Moodle, Blackboard Learn, and Schoology are a few popular LMSs utilised by educational institutions. iSpring Learn, Adobe Captivate Prime, Docebo LMS, TalentLMS, and eFront are a few well-known enterprise-level LMSs.
How does LMS work?

Common characteristics of an effective LMS include:
The users can access the LMS from any platform, including desktop, laptop, tablet, and smartphone, thanks to responsive design. The LMS should always show the version appropriate for the user’s selected device. The LMS should also enable content downloads so that users can access it even when offline.
User-friendly interface: Learners should be able to traverse effortlessly the LMS platform thanks to the user interface (UI). A confused or distracting user interface increases the risk of losing users and renders the LMS useless.
It includes Analytics and reporting tools for e-learning. Instructors and administrators must be able to view and track them to assess their online training programmes. Both individuals and learner groups can use this.
Management of the course catalogue and courses: The LMS houses the eLearning courses and their associated course materials. Administrators and instructors should be able to build and administer these catalogues to provide a more specialised learning experience,
Integration and interoperability of content: When one develops content developed and saved in an LMS, one must package using interoperable standards, such as SCORM and xAPI.
Assistance services: The degrees of support provided by various LMS vendors differ. Many offer online forums where people can interact and support one another. For an additional fee, additional support services are accessible, such as a dedicated toll-free service line.
Support for certification and compliance – Systems used for online compliance training and certifications must have this feature. The instructors and administrators should evaluate an individual’s skill set and should be able to pinpoint any performance gaps. Using LMS records in an audit will also be available, thanks to this feature.
Impact of LMS

Learning requirements are evolving. The act of learning is also.
The L&D department emphasises formal, top-down learning, organised via face-to-face meetings or official e-learning courses. As performance support, the emphasis now is on encouraging knowledge sharing inside a company and helping workers on the job.
The former presents an alternative viewpoint on the LMS.
It is no longer the only answer for corporate learning.
It is merely a component of the learning ecosystem.
More and more L&D teams are adopting a bottom-up strategy, allowing employees more control over their learning solutions rather than prescribed from above. For instance, subject matter experts (SMEs) within the organisation—typically employees—can generate the learning content themselves rather than outsourcing it to pricey instructional designers. The former strategy is called “employee-generated learning” (EGL).
The tools required to develop and maintain the information will severely impact this change.
It also has a significant impact on learning at the same time. In addition to the LMS, we also need tools to enhance performance and facilitate knowledge sharing; both need more contemporary strategies.
The world of e-learning has experienced a shift to the knowledge-sharing quadrant during the past few years, resulting in the trend of switching from top-down learning to peer knowledge sharing. The Learning Experience Platform (LXP), which enabled it, also grew in popularity. Moving closer to the performance support quadrant, we are now focusing on helping people at work.
These changes demand various learning-related tools for developing, updating, and disseminating learning materials.
Combining these instruments creates a learning environment. Also known as a learning ecosystem.
What is the LAMP approach?
The therapy strategy Language Acquisition via Motor Planning (LAMP) from motor learning and neuroscience; Giving nonverbal people or people with limited language skills a way to independently and spontaneously express themselves in every situation is the main objective.
John Halloran, MS’s clinical practises as the foundation for LAMP. CCC-SLP, Mia Emerson, MS, CCC-SLP, and Cindy Halloran, OTR/L. When they
contacted nonverbal autistic persons, they discovered that the following methods offered a way to foster independent communication:
a) Giving people access to key terms on a speech-generating system device,
b) Introducing those terms through sensory-rich exercises, and
c) Using a dependable, distinctive method to access each word on the gadget combines aural feedback and a motor pattern.
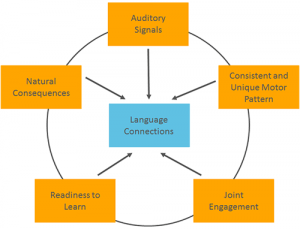
How does the LAMP approach work?

Impairments in motor abilities, auditory processing, and sensory integration may impact language and social interaction. Some of the interventions currently being used with autistic people concentrate on the traits seen as strengths, like visual learning and a need for structure.
In addition to utilising visual learning and the need for structure, the LAMP approach also addresses fundamental language delay deficiencies to enhance spontaneous, creative communication.
Language and communication are improved via LAMP by:
- Replacing the brain mechanisms involved in the production of ordinary speech
- Combining a regular motor action with regular aural feedback and a natural reaction.
One can use LAMP when employing a speech-generating apparatus without cognitive qualifications because intervention can start at the cause. One builds the stages of the formation of natural language at the cause and effect level.
Impact of Using LAMP Techniques

According to ongoing research, the following improvements happened when one utilises the LAMP techniques:
- Increased conversational spontaneity in any setting
- Using original word combinations
- Increased average utterance duration (MLU)
- The increased use of receptive vocabulary
- Using a variety of communication techniques
- More naturally occurring vocalisation
Although the method initially allowed nonverbal autistic people a way to communicate, it may be modified to help people with a range of difficulties.
Although each person will advance at a different rate, assuming competence is crucial to maximising potential. LAMP is a strategy for giving someone a language system that can progress from first words to fluent conversation; it is not a cure.
Conclusion
While each is highly useful for its specific purpose, there are significant differences between them. If you’re selecting, ensure that you thoroughly understand your options.
We’ve seen both in action, and the implementation of LAMP is much more effective. It caters to people with disabilities and allows instructors to make changes in “real-time” is remarkable.
The LMS continues to be a key component of sharing and distributing learning content. However, it is no longer the only choice.
It would be great to explore beyond this standard to satisfy the evolving demands of your students, whether by enhancing the tools you already use.
For any queries related to parenting, schooling, or any student-related tips, click here to check out our latest blogs